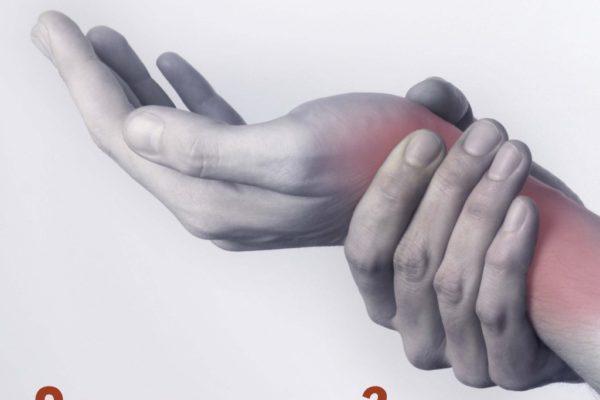
Joints work hard. They connect bones, allow movement, and provide support to other parts of the body. Joints take a lot of impacts and keep you in motion.
A joint that is injured, worn out, or affected by the disease can cause pain and get in the way of day-to-day activities. Many options exist for treating joint pain, depending on the severity and if the pain is acute or chronic. Understanding the best treatment option for you will help you get on the road to recovery faster.
Acute Pain
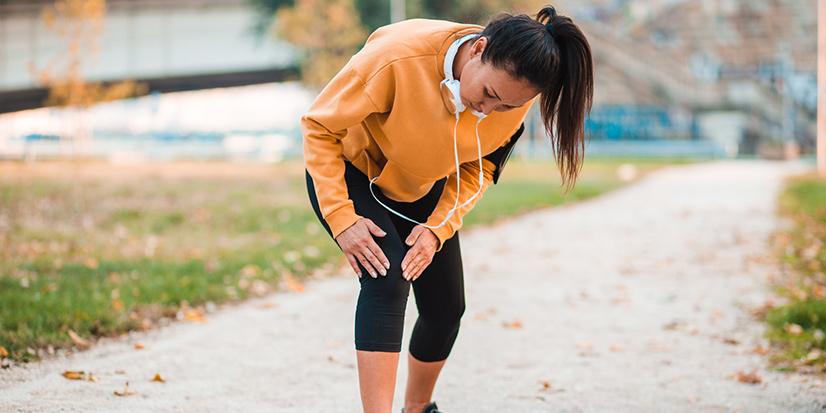
If pain is sudden or caused by injury, treatment can range from at-home care to medical interventions such as casting, bracing, or surgery.
- At-home Care: If your pain and symptoms are less severe, you should be able to manage them at home. Try the RICE method (rest, ice, compression, and elevation) along with an over-the-counter anti-inflammatory medication, such as Advil (ensure you take any medication as directed). Ice should be applied in 15-20 minute segments, once every few hours. If pain continues or worsens, consult your physician.
- Medical Care: If your pain is sharp and accompanied by inflammation, tenderness, and a sense of heat around the joint, you should schedule an appointment with your provider. If your pain is more severe and resulted from an injury, especially if you are unable to use your joint or it appears deformed, seeks immediate care. Visit the emergency room or urgent care when your joint can be assessed. Most likely, the provider will ensure your joint is stabilized and your pain is managed. Then, you will be referred to an orthopedic specialist who will take over your care plan.

Chronic Pain
If joint pain is something you’ve been dealing with for a long time, talk with your doctor to understand the cause. Some chronic pain is caused by a disease or ailment, such as arthritis, or it could stem from an old injury.
- Physical Therapy: If you have long-term pain, your doctor might recommend physical therapy. A physical therapist can work with you to strengthen the muscles around the joint and improve the range of motion. You might also see a physical therapist after having a joint replacement, or when recovering from injury.
- Weight Loss: Chronic joint pain can be more severe if you are overweight. Weight loss through diet and exercise can lessen the impact on your joints, helping to reduce pain. It is important to be cautious when starting a new exercise plan, especially if you are healing from an injury or have a medical condition. Scheduling a consultation with a health and wellness specialist is a good way to safely ease into a new routine.
- Joint Replacement: If your joint pain is chronic (long term) and if affects your day-to-day life, you may consider joint replacement. For the right candidates, joint replacement surgery can be the answer to your chronic pain and can help you get back to an active life.
For more information on how to care for your joints, visit altru.org/ortho.